The term “white label” generally refers to goods that are not marketed and sold under the brand of their actual manufacturer, but as products from other manufacturers.
Label fraud with an extra portion of service design
Examples of such white-label products can be found in every supermarket around the corner, without consumers being aware of it in most cases: From food, to clothing, to electronic devices, more products are made by a different manufacturer than is apparent at first glance. CD, DVD and Blue Ray blanks are a classic example of a white label product: numerous electronics retailers and supermarket chains sell blanks under their own brand name – with corresponding packaging design and branding on the data carrier itself. The actual manufacturer can only be read via the digital product code of the blank. Speaking of data carriers: we owe the term “white label” to the world of vinyl records and DJ culture. Before the public release of new records, copies without label details – i.e. with a white label – were sent to DJs and radio stations for promotional purposes. The term quickly became established in the DJ scene: successful DJs sometimes covered the records of their sets with white stickers so as not to reveal their musical sources to the DJ competition.

White label design in a digital environment
The white labeling strategy is also widely used in the digital sector. Here, the term stands for digital products and services whose appearance can be adapted to a certain extent to the requirements of the communicating brand. The technical infrastructure, the range of functions and the specific mode of operation are predefined by the white label provider and cannot be customized in most cases. The key feature of a digital white label solution is that it is experienced by end users as an independent product of the integrated brand and, ideally, no connection to the underlying provider is apparent. In the digital sector in particular, the focus is on outsourcing all technical expenses for licensees of a white label solution.
What are the benefits of white labeling?
The strategy of digital white labeling is primarily linked to economic considerations. A large number of potential savings and synergy effects speak in favor of white label solutions, both from the provider’s and the licensee’s point of view.
Advantages for providers of a white label solution:
- Multiple marketing and distribution of a product once developed
- Establishment of a long-term support and maintenance relationship with partners
- Ongoing further development of the product can be offered to all existing partners
- In addition to the business model of licensing and maintenance, there is also the option of transaction-based commission Scalable offers enable targeting of different partner target groups
Advantages for partners who use a white label solution:
- Very short time-to-market
- Significantly lower implementation costs than in-house development
- Outsourcing of technical implementation and maintenance
- Use of proven process, transaction and interaction design
- Immediate benefits through continuous product development
- High availability and reliability
- Scalability of functional scope and branding options enable customized solutions for different budgets and requirements
These are all requirements for a solid white label solution. What other unique selling points can there be for a product that is primarily characterized by its visual adaptability, i.e. its generic nature?
Learn
more
We are more than just experts – our dedicated team of designers, developers and marketing specialists work hand in hand to take your digital presence to the next level. Ready for the next step? Contact us and find out more about our services.
Digital Design minus Visual Design = Experience Design
If it is in the nature of a white label solution to have no characteristic interface and no specific visual design, where do we – as a design agency – see our scope for design? What remains if you subtract visual design from the overall “digital design” package? The answer lies in experience design: the central selling and application argument for products whose user interface can be replaced and customized must be a solid, tried-and-tested and functioning user experience and range of functions.
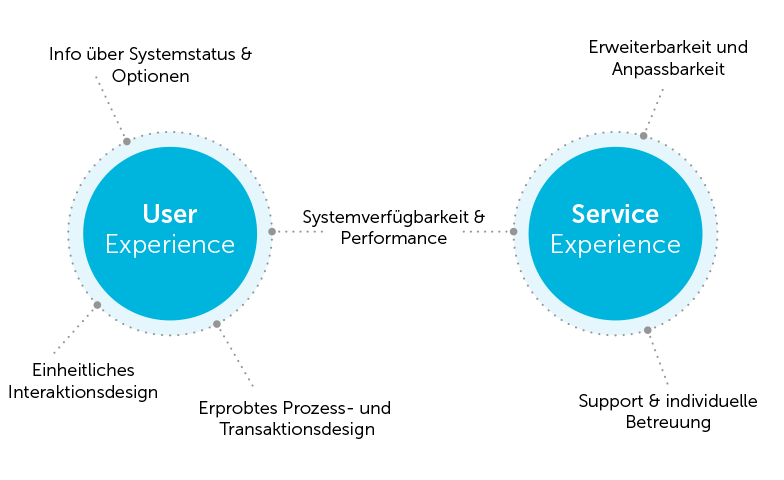
In this case, experience design includes several dimensions. On the one hand, topics relating to the user experience of the digital product are of central importance. On the other hand, the concept of experience design can be defined more broadly here and also include service design topics:
- Consistent interaction design: How does the system react to user actions?
- Clearly defined process and transaction design – how do processes and transactions work?
- Information about system status and options – how does the system communicate with its users?
- Technical service: system availability and performance
- Customization services: Extensibility and customizability
- Support and individual care
These design parameters make it possible to turn even a seemingly interchangeable product with a variable surface design into a convincing and unique service offering – for both licensees and end customers. At the core of convincing white label solutions are functionalities with proven interaction and transaction design as well as comprehensive service orientation.
Parameterization of design properties
The concrete design of a digital white label solution can only start after a detailed needs analysis of potential (end customer) target groups and the resulting definition of functional requirements. The design process begins with the search for the “lowest common denominator”: defining the visual design elements that define the digital product and determine its design identity. For one of our long-standing clients in the financial services sector, we carried out conceptual and strategic groundwork for a potential white label web solution. In this case, the “lowest common denominator” consisted of a list of very basic design assets that should make up the white label system to be developed. As the potential licensees of the system will have different brand requirements in terms of complexity, the focus was on a scalable design option for these assets based on a basic design.
From here, things get more detailed: detailed design parameters must be defined for all identified design elements as the project progresses. At the end of the process, there is a kind of style guide for all designable elements. Which design parameters are fixed and what can be adapted to brand and design requirements? In any case, the experience design remains the functional bracket of all white label client systems.
Do you need help with the conception, design and technical development of white label solutions? We are happy to support you with intelligent designs and technologies.
Stay
tuned
More articles




